In the current context of energy transition and growing awareness of green living, off-grid systems are becoming increasingly important for remote areas, off-grid households, and emergency applications. While standalone solar systems are mature and easy to install, they face limitations in power generation at night, on cloudy days, or in shaded areas. Wind power, on the other hand, can supplement electricity when solar resources are insufficient. This article provides a detailed overview of how to build a 10kW off-grid wind(Liam F1 Wind Turbine)–solar hybrid power system, discussing the benefits of hybrid technology, core component selection, system integration principles, and key considerations for installation and maintenance.
I. System Advantages
1.1 Importance of Energy Independence
-
Reducing Reliance: An off-grid system can reduce dependence on traditional power grids, avoiding the economic risks associated with rising electricity prices.
-
Environmental Benefits: By combining solar and wind—two renewable energy sources—you can significantly cut carbon emissions and contribute to a greener lifestyle.
1.2 Advantages of a Wind–Solar Hybrid System
-
Time-based Complementarity: Solar power is the main source of electricity during the day, while wind turbines can provide energy at night or on windy, cloudy days.
-
Environmental Complementarity: In suitable geographical locations, stable wind speeds can maximize wind generation, while good sunlight resources can fully leverage solar power.
-
Lower Battery Load: Combining two energy sources reduces deep discharges in the battery bank, extending overall system lifespan.
II. System Components
The system comprises the following major components:
-
Wind Turbine (e.g., Liam F1 Wind Turbine)
-
Wind Turbine Charge Controller
-
Solar Panel
-
Inverter
-
Lithium Battery
-
Solar Cable / Wind Cable
-
MC Connector
2.1 Liam F1 Wind Turbine
-
Key Features:
-
Spiral blade design that automatically orients with the wind, eliminating the need for a complex control system.
-
Compact, low-noise profile—ideal for rooftops or building walls.
-
Capable of starting at lower wind speeds, making it suitable for urban and moderate wind conditions.
-
- Use Case:
In off-grid hybrid systems, the Liam F1 Wind Turbine plays a critical role during nighttime or cloudy periods when solar is insufficient.
2.2 Wind Turbine Charge Controller
-
Function:
-
Regulates and protects the DC power generated by the wind turbine.
-
Prevents overcharging or over-discharging, prolonging battery life.
-
-
Selection Tips:
-
Ensure compatibility with the turbine’s output voltage/current; opt for MPPT functionality for maximum power utilization.
-
2.3 Solar Panel
-
Function & Benefits:
-
Converts sunlight into DC power and is the main power source during daylight hours.
-
Easy to install and maintain over the long term.
-
-
Design Recommendations:
-
Size your solar array according to local sunlight conditions and the system’s power requirements. Arrays of about 5–10kW are typical for a 10kW system.
-
2.4 Inverter
-
Function:
-
Converts stored DC power (from wind and solar) into AC power for household or commercial loads.
-
-
Selection Requirements:
-
Choose a hybrid inverter that accepts both wind and solar inputs.
-
Rated capacity should match the system’s peak power demand—around 10kW or higher.
-
2.5 Lithium Battery
-
Storage Role:
-
Stores excess power to ensure continuous supply when sources are insufficient.
-
-
Capacity Calculation:
-
Plan total battery storage based on average daily usage and reserve days (commonly 2–3 days).
-
For example, if your household uses 30kWh daily, consider at least 60–90kWh of storage.
-
2.6 Solar Cable and Wind Cable
-
Requirements:
-
Use high-quality, multi-stranded copper cables with low resistance, water resistance, heat resistance, and UV protection.
-
Voltage ratings of around DC1500V are common to ensure efficient energy transmission.
-
2.7 MC Connector
-
Function:
-
Quickly and stably connect solar panels with other system components to ensure overall system performance and safety.
-
Right after this sentence, here is the system configuration table:
| Ttem | Article | Specification | Number | Price | Total Price |
| 1 | Wind turbine 2000w
(Including blades, generator,and other screws) |
Rate Voltage:48V
Rate Power :2000W |
1 | $1,100.0 | $1,100.0 |
| 2 | Wind turbine
Charge Controller |
2000W/48V Wind turbine MPPT Charge Controller | 1 | $80.0 | $80.0 |
| 3 | Solar Panel 550W | Power:550W
Voltage:47.1V±3% |
16 | $68.0 | $1,088.0 |
| 4 | Inverter | 11KW
Input 48V Output 220V |
1 | $690.0 | $690.0 |
| 5 | Lithium Battery | 48v 200ah | 1 | $1,180.0 | $1,180.0 |
| 6 | Solar cable | PV4mm² | 100 | $0.5 | $50.0 |
| 7 | Wind cable | RV2.5mm² | 100 | $0.4 | $40.0 |
| 8 | MC connector | Rated current:30A
Rated voltage:1000DVC |
16 | $0.13 | $2.08 |
| 9 | $4,230.1 |
III. System Integration and Overall Design
3.1 Hybrid Power Operation Principle
-
Wind–Solar Complementarity:
-
Solar power is the main daytime source; wind takes over when solar is insufficient at night or in cloudy conditions.
-
-
Coordinated Battery Storage:
-
Dedicated charge controllers manage wind and solar MPPT to store energy in lithium batteries.
-
Once the battery reaches a certain level, the inverter converts DC to AC to power loads.
-
3.2 Intelligent Energy Management System (EMS)
-
Function:
-
Monitors wind, solar, battery, and load in real time, optimizing wind/solar charge distribution.
-
Remote monitoring helps identify and address anomalies early, ensuring stable long-term performance.
-
-
Technical Requirements:
-
Data acquisition, remote monitoring, and automatic control features enable consistent efficiency even under changing environmental conditions.
-
3.3 System Connection Diagram
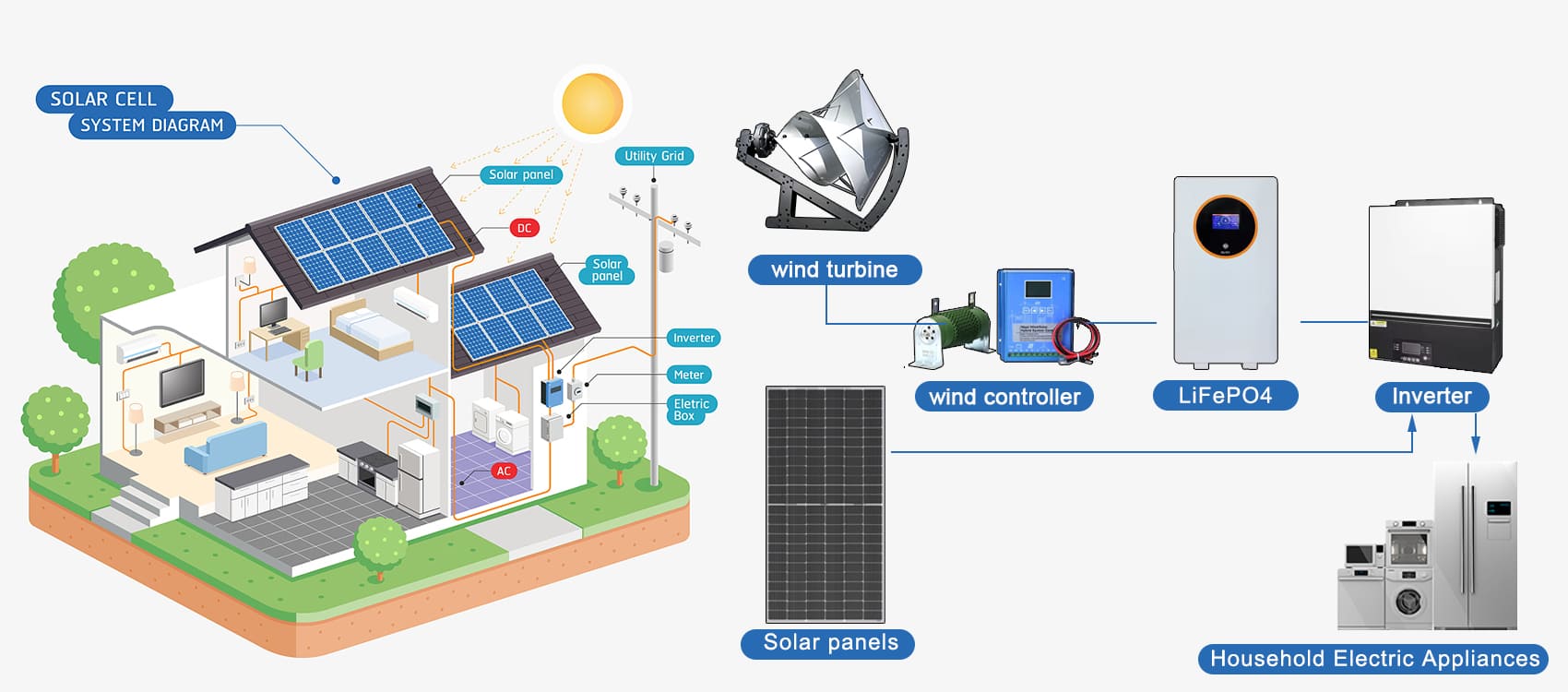
-
The connection between the Liam F1 Wind Turbine and its charge controller
-
Solar panels feeding the battery system through an MPPT controller
-
The battery system linking to the hybrid inverter
-
AC power output for household or business loads
IV. Installation and Maintenance Guidelines
4.1 Site Selection and Installation
-
Wind Turbine:
-
Place the Liam F1 Wind Turbine in an unobstructed area with higher wind speeds, e.g., a prominent rooftop space, to ensure effective wind capture.
-
-
Solar Panels:
-
Position them in the best orientation for your region (often facing south) and keep them free of shade or debris.
-
4.2 System Commissioning and Protection
-
Initial Setup:
-
Hire qualified technicians to verify system outputs and ensure the components meet specifications.
-
-
Safety and Protection:
-
Include overcharge, over-discharge, short-circuit, and overload protection;
-
Regularly inspect cables, connectors, and controllers for wear or aging parts that could affect safety or performance.
-
4.3 Daily Maintenance
-
Routine Cleaning:
-
Remove dust or debris from the solar panels and Liam F1 Wind Turbine blades to maintain generation efficiency.
-
-
Battery Monitoring:
-
Use your EMS to track battery temperature, voltage, and other key parameters, ensuring safe operation.
-
-
Parameter Adjustments:
-
Adjust system settings as needed based on local weather fluctuations, such as wind speed, solar irradiance, and temperature.
-

